| In vitro: |
| J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Jul 11;55(14):5869-74. | | Food-grade mulberry powder enriched with 1-deoxynojirimycin suppresses the elevation of postprandial blood glucose in humans.[Pubmed: 17555327 ] | Mulberry 1-Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), a potent glucosidase inhibitor, has been hypothesized to be beneficial for the suppression of abnormally high blood glucose levels and thereby prevention of diabetes mellitus. However, DNJ contents in commercial mulberry products were as low as about 0.1% (100 mg/100 g of dry product), implying that the bioavailability of DNJ might not be expected.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We carried out studies in two directions: (1) production of food-grade mulberry powder containing a maximally high DNJ content; (2) determination of the optimal dose of the DNJ-enriched powder for the suppression of the postprandial blood glucose through clinical trials. The following method was used: (1) DNJ concentrations in mulberry leaves from different cultivars, harvest seasons, and leaf locations were determined using hydrophilic interaction chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. (2) Healthy volunteers received 0, 0.4, 0.8, and 1.2 g of DNJ-enriched powder (corresponding to 0, 6, 12, and 18 mg of DNJ, respectively), followed by 50 g of sucrose. Before and 30-180 min after the DNJ/sucrose administration, plasma glucose and insulin were determined. The following results were obtained: (1) Young mulberry leaves taken from the top part of the branches in summer contained the highest amount of DNJ. After optimization of the harvesting and drying processes for young mulberry leaves (Morus alba L. var. Shin ichinose), DNJ-enriched powder (1.5%) was produced. (2) A human study indicated that the single oral administration of 0.8 and 1.2 g of DNJ-enriched powder significantly suppressed the elevation of postprandial blood glucose and secretion of insulin, revealing the physiological impact of mulberry DNJ (effective dose and efficacy in humans).
CONCLUSIONS:
This study suggests that the newly developed DNJ-enriched powder can be used as a dietary supplement for preventing diabetes mellitus. | | J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008 Oct;62(4):751-7. | | Novel anti-adherence activity of mulberry leaves: inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm by 1-deoxynojirimycin isolated from Morus alba.[Pubmed: 18565974 ] | The present study focused on isolation, characterization and evaluation of purified compounds from Morus alba against Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of crude extract from M. alba leaves was evaluated against oral pathogens, chiefly S. mutans. MICs were determined by the microdilution method. The compound was purified by employing silica gel chromatography and critically analysed with GC-MS, NMR and IR spectroscopy. The S. mutans traits of adherence and biofilm formation were assessed at sub-MIC concentrations of the crude extract and purified compound. Both water-soluble and alkali-soluble polysaccharide were estimated to determine the effect of the purified compound on the extracellular polysaccharide secretion of S. mutans. Its effect on biofilm architecture was also investigated with the help of confocal microscopy.
The purified compound of M. alba showed an 8-fold greater reduction of MIC against S. mutans than the crude extract (MICs, 15.6 and 125 mg/L, respectively). The extract strongly inhibited biofilm formation of S. mutans at its active accumulation and plateau phases. The purified compound led to a 22% greater reduction in alkali-soluble polysaccharide than in water-soluble polysaccharide. The purified compound was found to be 1-Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ). Confocal microscopy revealed that DNJ distorts the biofilm architecture of S. mutans.
CONCLUSIONS:
The whole study reflects a prospective role of DNJ as a therapeutic agent by controlling the overgrowth and biofilm formation of S. mutans. | | Molecules . 2016 Nov 23;21(11):1600. | | 1-Deoxynojirimycin: Occurrence, Extraction, Chemistry, Oral Pharmacokinetics, Biological Activities and In Silico Target Fishing[Pubmed: 27886092] | | Abstract
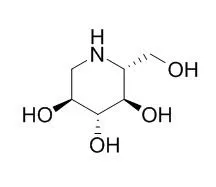
1-Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ, C₆H13NO₄, 163.17 g/mol), an alkaloid azasugar or iminosugar, is a biologically active natural compound that exists in mulberry leaves and Commelina communis (dayflower) as well as from several bacterial strains such as Bacillus and Streptomyces species. Deoxynojirimycin possesses antihyperglycemic, anti-obesity, and antiviral features. Therefore, the aim of this detailed review article is to summarize the existing knowledge on occurrence, extraction, purification, determination, chemistry, and bioactivities of DNJ, so that researchers may use it to explore future perspectives of research on DNJ. Moreover, possible molecular targets of DNJ will also be investigated using suitable in silico approach.
Keywords: Bacillus; anti-obesity; antihyperglycemic; antiviral; fermentation; iminosugar; molecular targets; mulberry; silkworms. | | Molecules . 2015 Dec 4;20(12):21700-14. | | 1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Insulin Resistance via Activation of Insulin Signaling PI3K/AKT Pathway in Skeletal Muscle of db/db Mice[Pubmed: 26690098] | | Abstract
1-Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ) is widely used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus as an inhibitor of intestinal α-glucosidase. However, there are few reports about its effect on insulin sensitivity improvement. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether DNJ decreased hyperglycemia by improving insulin sensitivity. An economical method was established to prepare large amounts of DNJ. Then, db/db mice were treated with DNJ intravenously (20, 40 and 80 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1)) for four weeks. Blood glucose and biochemical analyses were conducted to evaluate the therapeutic effects on hyperglycemia and the related molecular mechanisms in skeletal muscle were explored. DNJ significantly reduced body weight, blood glucose and serum insulin levels. DNJ treatment also improved glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance. Moreover, although expressions of total protein kinase B (AKT), phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), insulin receptor beta (IR-β), insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1) and glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) in skeletal muscle were not affected, GLUT4 translocation and phosphorylation of Ser473-AKT, p85-PI3K, Tyr1361-IR-β and Tyr612-IRS1 were significantly increased by DNJ treatment. These results indicate that DNJ significantly improved insulin sensitivity via activating insulin signaling PI3K/AKT pathway in skeletal muscle of db/db mice.
Keywords: 1-Deoxynojirimycin; GLUT4 translocation; PI3K/AKT; db/db mice; insulin resistance; insulin signaling pathway; mulberry leaves; skeletal muscle. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)