| In vitro: |
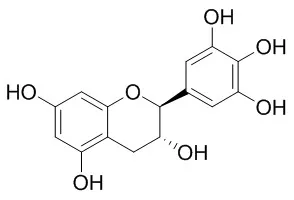
| J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117(39):9881-8. | | Antioxidant Potential of Gallocatechins. A Pulse Radiolysis and Laser Photolysis Study[Reference: WebLink] | Gallocatechins and catechins, which are constituents of green tea, and related, simpler single-ring model compounds undergo one-electron oxidation by the azidyl radical (k = (1.4-4.8) x 10(9) M(-1) s(-1)), which was used as a model one-electron, rapid oxidant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The initial oxidation leads to the formation of a mixture of A- and B- (or C-) ring phenoxyl radicals. This finding was confirmed by comparison with the spectra of 3,5-dihydroxyanisole (the model for A ring) and methyl gallate (the model for B or C ring) radicals and by photoionization experiments in which only the B-ring radical of epigallocatechin was generated, as expected from its lower ionization potential. The A-ring phenoxyl radical is converted to the B- (or C-) ring phenoxyl radical by inter- and intramolecular electron and proton transfer. The activation parameters clearly indicate solvent-assisted intermolecular electron and proton transfer, whereas intramolecular transfer in epigallocatechin gallate radicals is suggested to proceed through an intermediate molecular complex formation. Acid-base equilibria of parent gallocatechins (pK(al) > 8.0) are significantly altered in the corresponding phenoxyl radicals (pK(rl) = 4.4-5.5). The low reduction potentials of gallocatechin radicals, E(7) = 0.42 V (which is lower than that of vitamin E radicals, E(7) = 0.48 V), are responsible for their antioxidant efficacy, which may include the repair of vitamin E radicals. These low reduction potentials also imply high susceptibility of parent gallocatechins to rapid oxidation in aerated aqueous media. The reactivity of epigallocatechin gallate with superoxide radical at pH 7, k = 7.3 x 10(5) M(-1) s(-1) is one of the highest measured rates of reduction of superoxide radical by any chemical antioxidant. In this reaction, superoxide is converted to hydrogen peroxide, thus eliminating the redox cycling that may be involved in the corresponding oxidation reaction.
CONCLUSIONS:
The high rates of quenching of singlet oxygen by gallocatechins in acetonitrile, k = (1.1-2.2) x 10(8) M(-1) s(-1), are comparable to quenching by vitamin E, k = 5 x 10(8) M(-1) s(-1). | | 2015;38(2):325-30. | | Biotransformation of (-)-epigallocatechin and (-)-gallocatechin by intestinal bacteria involved in isoflavone metabolism[Pubmed: 25747993] | | Abstract
Four isoflavone-metabolizing bacteria were tested for their abilities to degrade (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC) and its isomer (-)-Gallocatechin (GC). Biotransformation of both EGC and GC was observed with Adlercreutzia equolifaciens JCM 14793, Asaccharobacter celatus JCM 14811, and Slackia equolifaciens JCM 16059, but not Slackia isoflavoniconvertens JCM 16137. With respect to the degradation of EGC, strain JCM 14793 only catalyzed 4'-dehydroxylation to produce 4'-dehydroxylated EGC (7). Strain JCM 14811 mainly produced 7, along with a slight formation of the C ring-cleaving product 1-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol (1). Strain JCM 16059 catalyzed only C ring cleavage to form 1. Interestingly, the presence of hydrogen promoted the bioconversion of EGC by these bacteria. In addition, strain JCM 14811 revealed the ability to catalyze 4'-dehydroxylation of 1 to yield 1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-ol (2) in the presence of hydrogen. In the case of GC, strain JCM 14793 mainly produced C ring-cleaving product (1) with only a very small amount of 4'-dehydroxylated GC (8), while Strain JCM 14811 only catalyzed 4'-dehydroxylation to form 8. Strain JCM 16059 formed 1. The bioconversion of GC by the three strains was stimulated by hydrogen. Strain JCM 14793 showed the ability to convert 1 into 2 in the presence of hydrogen as did strain JCM 14811. Furthermore, strains JCM 14793 and JCM 14811 were found to have the ability to catalyze p-dehydroxylation of the pyrogallol moiety in the EGC metabolites 4-hydroxy-5-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)valeric acid (3) and 5-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone (4), and this ability was enhanced by the presence of hydrogen. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)