| Animal Research: |
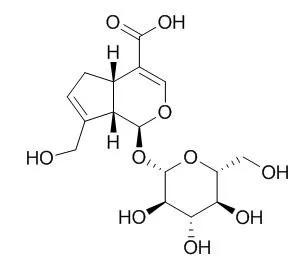
| Pharm Biol. 2015 Feb;53(2):280-5. | | Anti-atherosclerotic effect of geniposidic acid in a rabbit model and related cellular mechanisms.[Pubmed: 24963945] | Geniposidic acid, one of the main active ingredients in Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis (Rubiaceae), may also possess important pharmacological activities for cardiovascular disorders similar to other derivatives, such as geniposide.
To evaluate its anti-atherosclerosis (anti-AS) effect, the related pharmacological activities and possible cellular mechanisms were studied.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Thirty rabbits were randomly divided into normal control group, model control group, and Geniposidic acid subgroups. In the AS model, its effects on the intima/media thickness ratio and aortic morphology were observed. In the study of primary cultured endothelial cells (ECs) and human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells (HUASMCs), its activities on both ECs and HUASMCs proliferation, HUASMCs' migration were also studied.
Compared with the model control group, the plaque area, intima/media thickness ratio, and intimal foam cells number in Geniposidic acid (80, 160, and 240 mg/kg) subgroups were significantly improved (p < 0.05). By HE staining, the activities of Geniposidic acid on relieving ECs shedding and improving aortic morphology disorders were also demonstrated. From the results of CCK-8 testing, only 100 μg/ml Geniposidic acid performed significant inhibition on SMC proliferation. The relative IC50 of Geniposidic acid on SMC inhibition was 87.73 μg/ml. Geniposide acid also showed promotion effect on ECs proliferation, and the related ED50 of Geniposidic acid was 86.05 μg/ml. Besides, only 50 and 100 μg/ml Geniposidic acid showed obvious inhibition on SMC migration from the upper chamber (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
The effects of Geniposidic acid on protecting vascular endothelium and reversing plaque formation in an atherosclerotic model were demonstrated. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:197-207. | | Geniposidic acid protected against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and acute intrahepatic cholestasis, due to Fxr-mediated regulation of Bsep and Mrp2.[Pubmed: 26723467] | Geniposidic acid (GPA) is the main constituent of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae), which has long been used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders. The cholagogic effect of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) and GPA have been widely reported, but the underlying occurrence mechanism remains unclear.
This investigation was designed to evaluate the hepatoprotection effect and potential mechanisms of GPA derived from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) on fighting against α-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) caused liver injury with acute intrahepatic cholestasis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were intragastrically (i.g.) administered with the GPA (100, 50 and 25mg/kg B.W. every 24h) for seven consecutive days, and then they were treated with ANIT (i.g. 65mg/kg once in the 5th day) which induced liver injury with acute intrahepatic cholestasis. Serum and bile biochemical analysis, bile flow rate and liver histopathology were measured to evaluate the protective effect of GPA fight against ANIT treatment. The protein and mRNA expression levels of farnesoid X receptor (Fxr), bile-salt export pump (Bsep), multidrug resistance associated protein2 (Mrp2), were evaluated to study the effect of liver protection about GPA against ANIT induced hepatotoxicity and underlying mechanisms.
Some abnormalities were observed on ANIT treated rats including weight loss, reduced food intake and hair turned yellow. Obtained results demonstrated that at dose 100 and 50mg/kg B.W. (P<0.01) and 25mg/kg B.W. (P<0.05) of GPA pretreated dramatically prevented ANIT induced decreased in bile flow rate. Compared with ANIT treated group, the results of bile biochemical parameters about total bile acid (TBA) was increased by GPA at groups with any dose (P<0.01), glutathione (GSH) was increased significantly at high dose (P<0.01) and medium dose (P<0.05), total bilirubin (TB) was increased at high and medium dose (P<0.05), direct bilirubin (DB) was only increased at high dose (P<0.01). Serum levels of glutamic-Oxalacetic transaminase (GOT), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT), γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (γ-GT), TB, DB and TBA in comparison with ANIT treated group (P<0.01) were reduced by GPA (between 100 and 50mg/kg B.W.) pretreatment. Histopathology of the liver tissue showed that pathological damages and hepatic portal area filled with bile were relieved after GPA pretreatment compared with ANIT treated group. The protein and mRNA expression of Fxr, Bsep and Mrp2 were decreased in ANIT treated group. On the contrary, the protein and mRNA of Fxr, Bsep and Mrp2 were up regulated significantly pretreatment by GPA at dose of high and medium groups. On protein level of Bsep and Mrp2 the result shown no statistical difference in GPA (25mg/kg B.W.), but it was not same shown in mRNA level.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of this investigation have demonstrated that the GPA exerts a dose dependent hepatoprotection effect on ANIT induced liver damage with acute intrahepatic cholestasis in rats, which may due to Fxr mediated regulation of bile transporters like Bsep and Mrp2. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)