L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
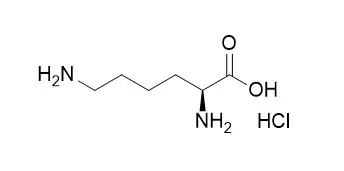
ChemFaces products have been cited in many studies from excellent and top scientific journals
Contact Us
Order & Inquiry & Tech Support
Tel: (0086)-27-84237683
Tech: service@chemfaces.com
Order: manager@chemfaces.com
Address: 176, CheCheng Eest Rd., WETDZ, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
How to Order
Orders via your E-mail:
1. Product number / Name / CAS No.
2. Delivery address
3. Ordering/billing address
4. Contact information
Order: manager@chemfaces.com
Delivery time
Delivery & Payment method
1. Usually delivery time: Next day delivery by 9:00 a.m. Order now
2. We accept: Wire transfer & Credit card & Paypal
Citing Use of our Products
* Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). We shipped via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS and others courier.
According to end customer requirements, ChemFaces provide solvent format. This solvent format of product intended use: Signaling Inhibitors, Biological activities or Pharmacological activities.
| Size /Price /Stock |
10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO / $7.0 / In-stock |
Other Packaging |
*Packaging according to customer requirements(100uL/well, 200uL/well and more), and Container use Storage Tube With Screw Cap |
More articles cited ChemFaces products.
- Cell Physiol Biochem....2017...
- Journal of Oil Palm Research...2019...
- Evid Based Complement Alternat Me...2017...
- Exp Parasitol.2018, 194:67-78
- Gene.2022, 815:146178.
- Dicle Tip Dergisi2020, 47(2),423-430.
- Biochem Pharmacol.2020, 178:114083
- Korean J of Pharmacognosy...2020...
- Wageningen University & Research...2018...
- Chem Res Toxicol. ...2022...
- Invest New Drugs.2017, 35(2):166-179
- Int J Cosmet Sci....2022...
- Journal of Third Military Medical...2019...
- Mol Cell.2017, 68(4):673-685
- Phytother Res.2020, 34(4):788-795.
- LWT2021, 147:111620.
- Food Chem.2021, 360:130063.
- Sci Rep. 2018, 1-9
- Molecules.2022, 27(21):7514.
- Phytomedicine.2018, 40:37-47
- Comparative Clinical Pathology ...2021...
- Molecules.2019, 24(1):E159
- Phytother Res.2019, 33(7):1784-1793
- More...
Our products had been exported to the following research institutions and universities, And still growing.
- University of Limpopo (South Africa)
- China Medical University (Taiwan)
- Universidade do Porto (Portugal)
- Macau University of Science and... (China)
- Leibniz Institute of Plant Bioc... (Germany)
- Washington State University (USA)
- Korea Intitute of Science and T... (Korea)
- Chiang Mai University (Thailand)
- University of Beira Interior (Portugal)
- Centralised Purchases Unit (CPU... (India)
- Regional Crop Research Institute (Korea)
- More...




 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)