| In vitro: |
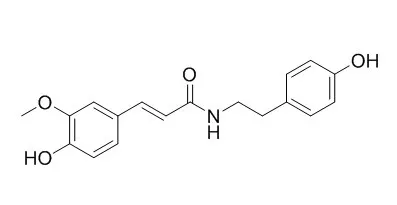
| Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jun 25;235:56-62. | | N-trans-feruloyltyramine inhibits LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Involvement of AP-1 and MAP kinase signalling pathways.[Pubmed: 25843058] | Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway can regulate inflammatory and immune responses. N-trans-Feruloyltyramine (FLA) is an active phenylpropanoid compound.
It possesses antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-melanogenesis, and anticancer activities. However, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying FLA modulation of cytokine expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages have not been fully investigated. In this study, we examined the mechanisms underlying the immunomodulative effects of FLA isolated from Arcangelisia gusanlung.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
FLA strongly suppressed mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), but not tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, thereby inhibiting the production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Furthermore, FLA also inhibited nuclear translocation of activation protein (AP)-1, and simultaneously decreased the expression and phosphorylation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) protein.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of FLA might be attributed to downregulation of COX-2 and iNOS via suppression of AP-1 and the JNK signalling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. | | Fitoterapia. 2010 Mar;81(2):124-31. | | Antioxidant and enzyme inhibition activities and chemical profiles of Polygonum sachalinensis F.Schmidt ex Maxim (Polygonaceae).[Pubmed: 19698767] | Polygonum sachalinensis is a widespread invasive plant in Europe. Chemical profiles of its different organs were studied by HPLC-UV-ESI/MS.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Seven major constituents quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside, lapathoside D, N-trans-Feruloyltyramine, lapathoside C, hydropiperoside, and vanicoside B were isolated and identified. The free radical-scavenging, alpha/beta-glucosidase, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of crude MeOH extracts and isolated compounds were studied. The structure-activity relationships were discussed. The chemical profiles revealed flavonoids and phenylpropanoids are the major compounds of all the organs of this plant. Quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside, lapathoside D, N-trans-Feruloyltyramine, lapathoside C and hydropiperoside were isolated from this species for the first time. In the alpha-glucosidase bioassay, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside, lapathoside D and N-trans-Feruloyltyramine demonstrated stronger activities than the positive reference acarbose.
CONCLUSIONS:
The trend in scavenging power showed no relation to enzyme inhibition in the test models. | | Inflamm Res . 2018 Jan;67(1):67-75. | | Nature is the best source of anti-inflammatory drugs: indexing natural products for their anti-inflammatory bioactivity[Pubmed: 28956064] | | Abstract
Objectives: The aim was to index natural products for less expensive preventive or curative anti-inflammatory therapeutic drugs.
Materials: A set of 441 anti-inflammatory drugs representing the active domain and 2892 natural products representing the inactive domain was used to construct a predictive model for bioactivity-indexing purposes.
Method: The model for indexing the natural products for potential anti-inflammatory activity was constructed using the iterative stochastic elimination algorithm (ISE). ISE is capable of differentiating between active and inactive anti-inflammatory molecules.
Results: By applying the prediction model to a mix set of (active/inactive) substances, we managed to capture 38% of the anti-inflammatory drugs in the top 1% of the screened set of chemicals, yielding enrichment factor of 38. Ten natural products that scored highly as potential anti-inflammatory drug candidates are disclosed. Searching the PubMed revealed that only three molecules (Moupinamide, Capsaicin, and Hypaphorine) out of the ten were tested and reported as anti-inflammatory. The other seven phytochemicals await evaluation for their anti-inflammatory activity in wet lab.
Conclusion: The proposed anti-inflammatory model can be utilized for the virtual screening of large chemical databases and for indexing natural products for potential anti-inflammatory activity.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Bioactivity index; Chemoinformatics; Ligand-based modeling. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)