| In vitro: |
| Arch Pharm Res. 2016 May;39(5):713-20. | | Anti-osteoclastogenic effects of isoquinoline alkaloids from the rhizome extract of Sinomenium acutum.[Pubmed: 26992921 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A phytochemical investigation for the rhizome extract from Sinomenium acutum (Menispermaceae) resulted in the isolation of several active principles responsible for the anti-osteoclastogenic property of the extract, together with related isoquinoline alkaloids (1-13) including two new compounds, 1 and 2. Among isolated compounds, salutaridine (7), dauricumine (10), Cheilanthifoline (12), and dauriporphine (13) were observed to give significant inhibitions on receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages into multinucleated osteoclasts, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
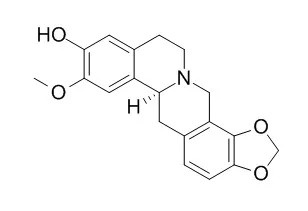
The chemical structures of two newly isolated compounds, 1 and 2 were established as 8-demethoxycephatonine (1) and 7(R)-7,8-dihydrosinomenine (2), by spectroscopic analyses including 2D NMR experiments. | | Phytother Res. 2010 Apr;24(4):481-5. | | Antiplasmodial agents from the Bhutanese medicinal plant Corydalis calliantha.[Pubmed: 19496064 ] | The alkaloidal components of the Bhutanese medicinal plant Corydalis calliantha Long, which is used for the treatment of malaria, have been assessed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four known alkaloids, protopine (1), scoulerine (2), Cheilanthifoline (3) and stylopine (4) are reported from this plant for the first time. The protopine alkaloid, protopine, and the tetrahydroprotoberine alkaloid, Cheilanthifoline, showed promising in vitro antiplasmodial activities against Plasmodium falciparum, both wild type (TM4) and multidrug resistant (K1) strains with IC(50) values in the range of 2.78-4.29 microM. Such activity had not been demonstrated previously for Cheilanthifoline.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results thus support, at a molecular level, the clinical use of this plant in the Bhutanese traditional medicine and identified Cheilanthifoline as a potential new antimalarial drug lead. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)