| Structure Identification: |
| J Nat Prod. 2009 Aug;72(8):1497-501. | | Sesquiterpene lactones from the root tubers of Lindera aggregata.[Pubmed: 19639966] |
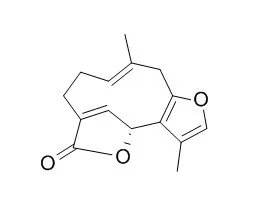
Phytochemical investigation of the root tubers of Lindera aggregata resulted in the isolation of five new sesquiterpene lactones, linderagalactones A-E (1-5), along with eight known sesquiterpenoids, 3-eudesmene-1beta,11-diol, hydroxylindestenolide, strychnistenolide, hydroxyisogermafurenolide, atractylenolide III, linderane, neoLinderalactone, and Linderalactone.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures and relative configurations of 1-5 were determined by spectroscopic methods, especially HRESIMS and 2D NMR techniques. The absolute configurations of 1-4 were defined by comparison of quantum chemical TDDFT calculated and experimental ECD spectra. Linderagalactone A (1) is a halogenated sesquiterpene lactone possessing a unique rearranged carbon skeleton. Linderagalactone E (5), linderane, hydroxylindestenolide, and Linderalactone showed hepatoprotective activity against H2O2-induced oxidative damages on HepG2 cells with EC(50) values of 67.5, 167.0, 42.4, and 98.0 microM, respectively. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2001 Nov;26(11):765-7. | | Studies on constituents of the leaves of Lindera aggregata (Sims) Kosterm.[Pubmed: 12776349] | To study the antibacterial and anti-inflammatory constituents of the leaves of Lindera aggrega.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Compounds were isolated by colum chromatography, and the structures were identified by spectroscopic methods.
Six compounds were isolated and identified as mixture of 6-Acetyllindenanolide B-1 and B-2(I), dehydrolindestrenolide (II), hydroxylinderstrenolide (III), Linderalactone (IV), kameofero (V), beta-sitosterol (VI).
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds were obtained from the leaves of Lindera aggregata for the first time. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)