| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2013, 44(3):313-319. | | The Constituents from the Stems of Annona cherimola.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
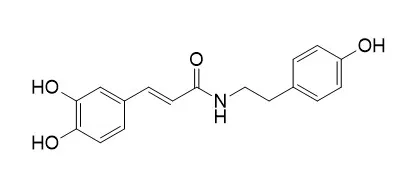
Thirty‐five compounds including twenty‐one alkaloids, lysicamine (1 ), liriodenine (2 ), atherospermidine (3 ), oxoxylopine (4 ), oxoanolobine (5 ), oxoglaucine (6 ), (‐)‐anonaine (7 ), (‐)‐asimilobine (8 ), (‐)‐xylopine (9 ), (‐)‐anolobine (10 ), (‐)‐norisocorydine (11 ), (+)‐laurotetanine (12 ), (+)‐isocorydine (13 ), (‐)‐N‐methylasimilobine (14 ), (+)‐N‐methyllaurotetanine (15 ), (‐)‐norushinsunine (16 ), (‐)‐ushinsunine (17 ), (‐)‐N‐formylanonaine (18 ), (+)‐stepharine (19 ), (+)‐orentaline (20 ), and (‐)‐kikemanine (21 ); four kauranes, ent‐kaur‐16‐en‐19‐oic acid (22 ), 16β‐hydroxy‐17‐acetoxy‐ent‐kauran‐19‐al (23 ), 17‐acetoxy‐16β‐ent‐kauran‐19‐oic acid (24 ), and 16β‐hydroxy‐17‐acetoxy‐ent‐kauran‐19‐oic acid (25 ); two amides, N‐trans‐femloyltyramine (26 ), and N-trans-caffeoyltyramine (27 ); one purine, adenosine (28 ); one lactam amide, squamolone (29 ); and six steroids, β‐sitosterol (30 ), stigmasterol (31 ), β‐sitostenone (32 ), stigmasta‐4,22‐dien‐3‐one (33 ), 6β‐hydroxy‐β‐sitosterone (34 ), and 6β‐hydroxystigmasterone (35 ) are isolated from the stems of Annona cherimola.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds were characterized and identified by physical and spectral evidence. Among them, (‐)‐norisocorydine (11) was elucidated as a new enantiomer with a levorotary configuration, which is isolated for the first time. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)