| Description: |
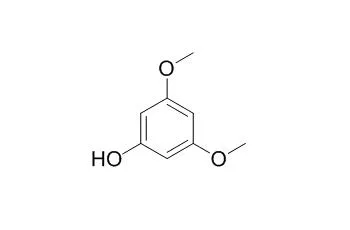
3,5-Dimethoxyphenol, a cyanogenic aglylactone considered as a marker of Taxus poisoning, being present in all species of Taxus. It has potent tyrosinase-inhibiting activity. |
| Targets: |
Tyrosinase |
| In vitro: |
| Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Mar;126(3):173-7. | | Synthesis and cosmetic whitening effect of glycosides derived from several phenylpropanoids.[Pubmed: 16508241] | Plant-derived phenylpropanoid compounds (4-ethyl-2-methoxyphenol, 2,6-dimethoxyphenol, 2,3-dimethoxyphenol, 3,4-dimethoxyphenol, 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol, 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, and 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid) were glycosidated to form glycoside compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We evaluated the effects of these compounds on the inhibition of tyrosinase and melanin synthesis and their cytotoxicity from the viewpoint of their use as whitening agents in cosmetics.
CONCLUSIONS:
Some compounds had more potent tyrosinase-inhibiting activity than commercial arbutin, which was used as a control, and showed no cytotoxicity at low concentration ranges. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Anal Toxicol. 2010 Jan-Feb;34(1):53-6. | | Preliminary gas chromatography with mass spectrometry determination of 3,5-dimethoxyphenol in biological specimens as evidence of taxus poisoning.[Pubmed: 20109304] | Taxus baccata is a widely distributed yew often associated with cases of fatal intoxication, which is related to the high amounts of cardiotoxic alkaloids, taxine A and taxine B, contained in its leaves.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this paper, a case of Taxus fatal poisoning, hypothesized by the forensic autopsy, has been confirmed by the application of both gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) techniques. A GC-MS method was used for the determination of the derivatized 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol, a cyanogenic aglylactone considered as a marker of Taxus poisoning, being present in all species of Taxus.
CONCLUSIONS:
The detection by LC-MS-MS of taxine B and isotaxine B in the biological specimens confirmed the absorption of cardiotoxic alkaloids and allowed to established the cause of death as the ingestion of Taxus baccata leaves. |
|



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)